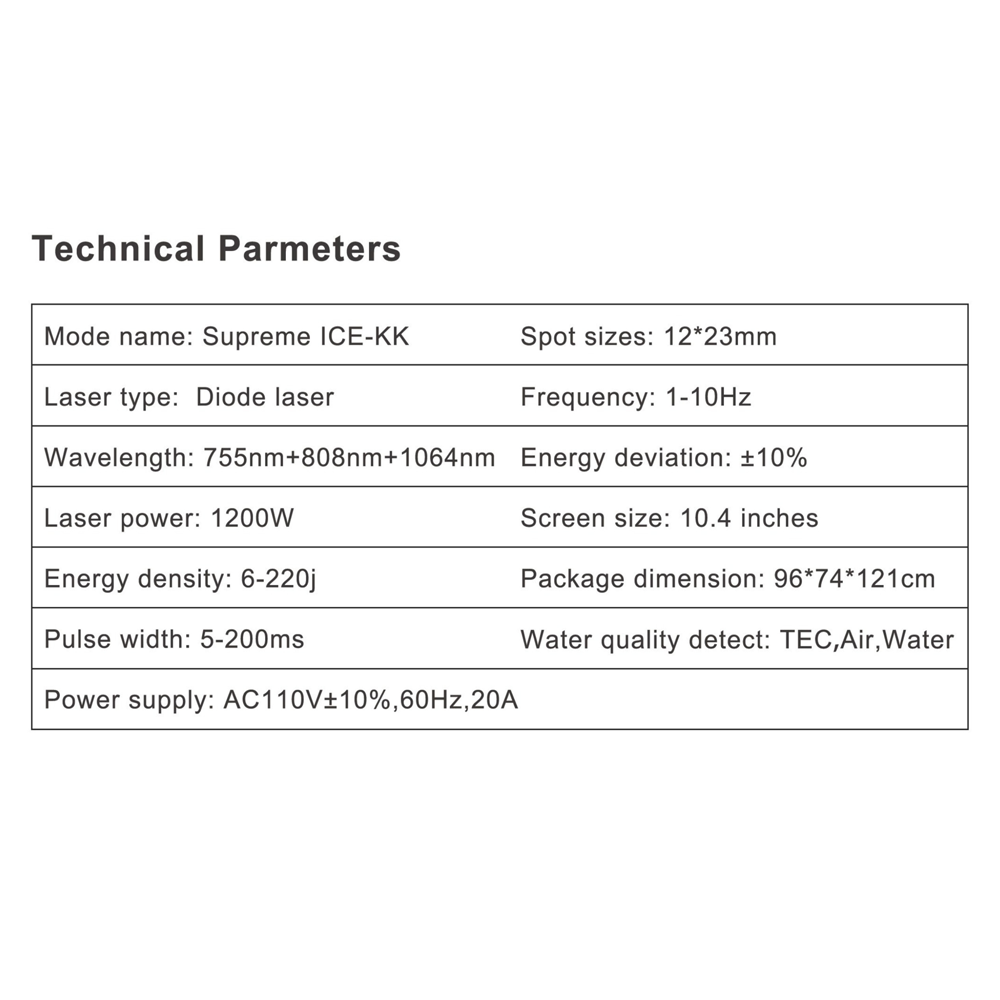
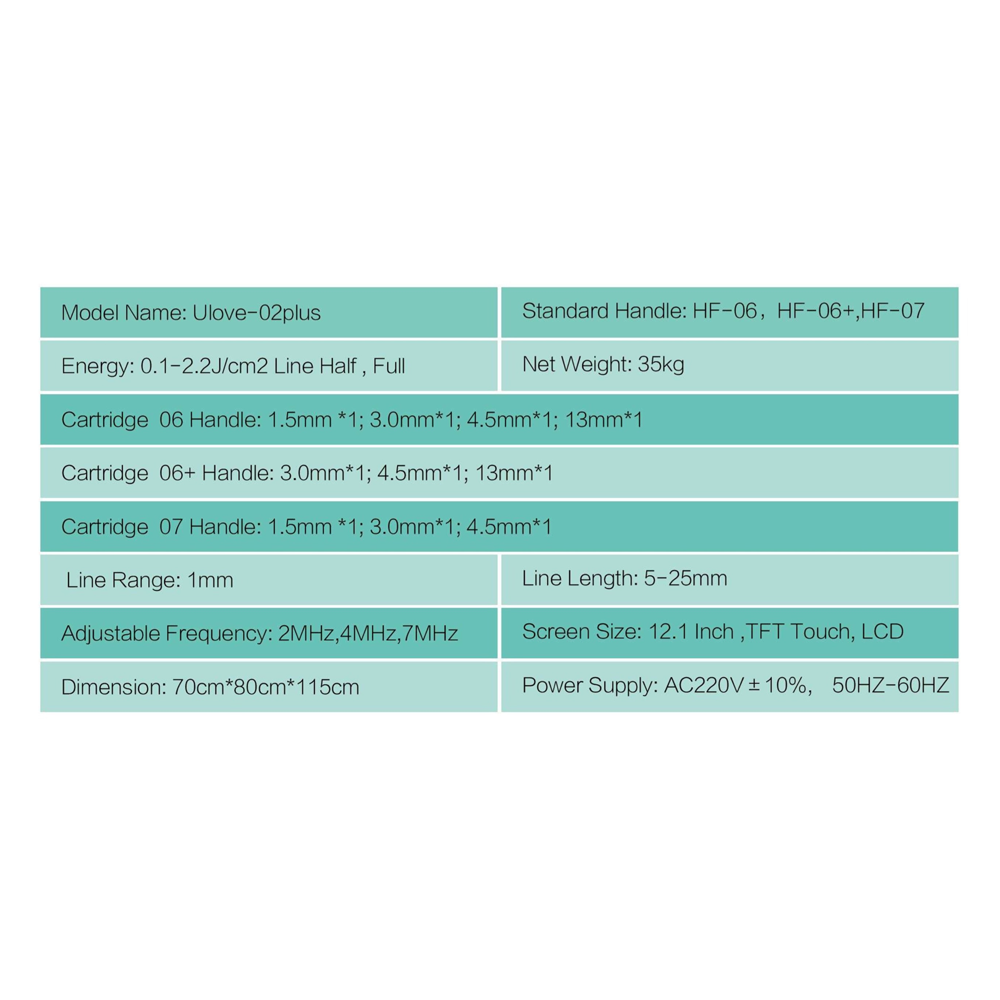
Laser technology has transformed many fields, from medicine to manufacturing. It uses focused light beams to accomplish tasks with precision and speed. Laser technology is essential for surgical procedures, cutting materials, and even in everyday devices like barcode scanners.
The versatility of lasers makes them valuable tools in various industries. They can perform delicate surgeries, create high-quality images, and enhance communication systems. Understanding how lasers work can help people appreciate their importance in modern life.
As technology advances, new applications continue to emerge. This means lasers are likely to play an even larger role in the future. Readers will discover the exciting possibilities of laser technology and its impact on society.
Fundamentals of Laser Technology
Laser technology is based on specific physical principles and comprises key components that allow it to function effectively. Various types of lasers exist, each serving different purposes across industries. Understanding the core aspects of lasers provides insight into their applications.
Physics of Lasers
Lasers work through a process called stimulated emission. When atoms or molecules gain energy, they can emit light. In a laser, this light is amplified through a medium, such as gas, liquid, or solid.
The emitted light is coherent, meaning it travels in a tight beam. This coherence allows lasers to be focused over long distances without spreading out. The wavelength of the light determines its color and affects its interaction with materials.
Key principles include:
- Population Inversion: More atoms in an excited state than in a lower energy state.
- Feedback Mechanism: Mirrors reflect light to boost amplification.
- Optical Cavity: The space between mirrors where the light bounces and grows stronger.
Main Components
Lasers have several main components that are crucial to their operation. These include:
- Gain Medium: This is the material where light amplification occurs. It can be a gas, liquid, or solid.
- Energy Source: Often called a pump, this provides energy to excite the atoms in the gain medium.
- Optical Cavity: Contains the mirrors that reflect light back and forth, enabling amplification.
Additional components may also include:
- Output Coupler: A partially reflective mirror allowing some light to escape.
- Cooling System: Keeps the system at suitable temperatures for optimal performance.
Different Types of Laser Technology
Lasers can be classified into different types based on their gain medium and applications. Some common types are:
- Gas Lasers: Use gas as the gain medium, like helium-neon lasers. They produce visible light.
- Solid-State Lasers: Utilize solid materials, such as ruby or Nd. These are versatile and powerful.
- Fiber Lasers: Incorporate optical fibers to deliver laser light. They are compact and efficient.
- Semiconductor Lasers: Based on semiconductor materials, these are commonly found in electronics.
Each laser type has unique characteristics, strengths, and uses, making them suitable for various applications in medicine, manufacturing, and telecommunications.
Key Application of Laser Technology
Laser technology has many important uses across different fields. It plays a critical role in medicine, industry, communication, and research. Each application showcases how versatile and useful lasers can be.
Medical Procedures
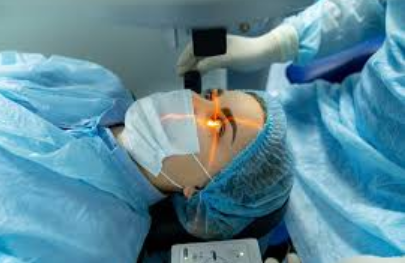
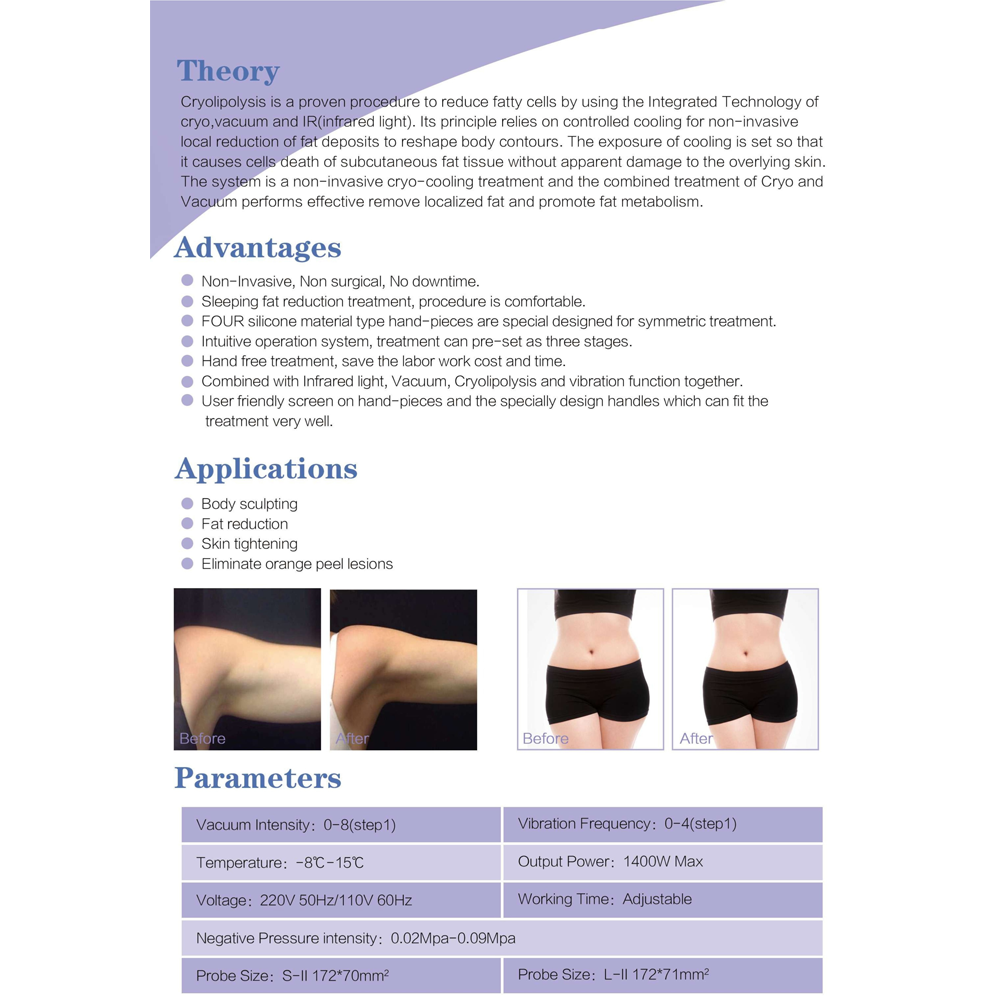
Lasers are widely used in various medical treatments. They help with eye surgeries, like LASIK, to correct vision. In dermatology, lasers treat skin conditions such as scars, wrinkles, and tattoos. They can also remove kidney stones and tumors with precision, reducing recovery time and complications.
In dental procedures, lasers help in reducing pain and improving accuracy. They can be used to remove cavities, reshape gums, and whiten teeth. Many doctors prefer lasers due to their ability to target specific areas while causing minimal damage to surrounding tissues.
Industrial Uses
Lasers are valuable tools in industrial settings. They are commonly used for cutting, welding, and engraving materials like metal, plastic, and wood. Their precision allows for clean cuts and detailed designs, which improves product quality.
In manufacturing, lasers can measure distances and inspect products with high accuracy. They enhance automation by guiding machines in complex tasks. This efficiency can lead to significant cost savings and faster production times.
Communication Systems
In communication systems, lasers are used for transmitting data. Fiber optic technology relies on lasers to send signals over long distances with speed and clarity. This method improves internet connections and phone signals.
Lasers are also essential in satellite communication and data centers. They help manage and transfer large amounts of information quickly. Their ability to maintain signal integrity makes them a preferred choice for modern communication networks.
Research and Development
Lasers play an important role in research and development across various fields. In scientific labs, they are used for experiments like spectroscopy and holography. This helps scientists analyze materials and study different properties.
In physics, lasers are crucial for studying atomic and molecular structures. They allow scientists to achieve precise measurements and create new technologies. Researchers also explore lasers for future applications, such as advanced manufacturing techniques and medical innovations.
Lasers continue to shape the future of many industries and scientific studies. Their diverse applications demonstrate their value in everyday life and high-tech fields.
Lasers in Consumer Electronics
In addition, consumer electronics also have a lot of applications for lasers. From barcode readers to DVD players, 3D printers, and beyond, there are devices based on laser systems. Indeed, with laser sintering technology, 3D printing can create highly detailed, customised product models, layer by layer.
Applications:
- Barcode scanners for retail
- DVD and Blu-ray players
- 3D printing is being used in custom products.
Future of Laser Technology
There are constant breakthroughs in laser technology. In the future, lasers will undoubtedly become even more remarkable. The following are some of the most exciting innovations in laser technology:
Quantum Lasers and Computing
Quantum lasers paired with quantum computing have the potential to transform data processing. We can expect exciting breakthroughs that might revolutionise everything from cybersecurity to artificial intelligence in the near future, as scientists create more efficient quantum lasers.
Laser-Powered Cars
With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), instead of charging stations, people may consider charging their electric vehicles through laser technology. Laser-powered, wireless EV charging systems are also going in the light of research.
Improved Medical Applications
Laser advancements may continue to progress in medicine. From treatment for laser eye surgery to new cancer therapies, lasers may become even more targeted and effective in the near future, helping millions achieve better healthcare.
Laser Safety Standards
Laser technology has become an essential and amazing part of our life, but lasers are not completely harmless. We rigorously follow laser safety standards to ensure a workplace free from accidents and injuries.
Key Safety Tips:
- Laser beams can harm your eyes, so make sure to put on goggles.
- Make sure only trained personnel use all the lasers.
- Place warning signs in areas where lasers are in use.
CONCLUSION:
The laser technology landscape changes rapidly every day across all sectors, including Optics Valley, a sector that only existed a few years ago. Lasers have shown versatility and usefulness, whether in laser cutting technology, research laser systems, or life-saving medical laser technology.
Looking forward, the future of lasers promises even more exciting possibilities. The applications range from quantum lasers able to drive emerging computing architectures to laser-mediated medical therapies with unparalleled precision.
Laser technology is a game changer for industries that want to become more efficient, safety focused, and innovative for the future. Lasers now serve as a tool to explore the future of science, industry, and healthcare.